Description
Labetalol is a competitive antagonist at Beta 1and Beta 2 adrenoreceptors and has some intrinsic activity at Beta 2 adrenoreceptors. Labetalol has, in addition to its Beta
blocking action, a competitive antagonist action at postsynaptic a. adrenoreceptors. In isolated tissues Labetalol is four to eight times more potent at p than a.-adrenoreceptors.
Indications
Tablet: Labetalol tablets are indicated for the treatment of all forms of
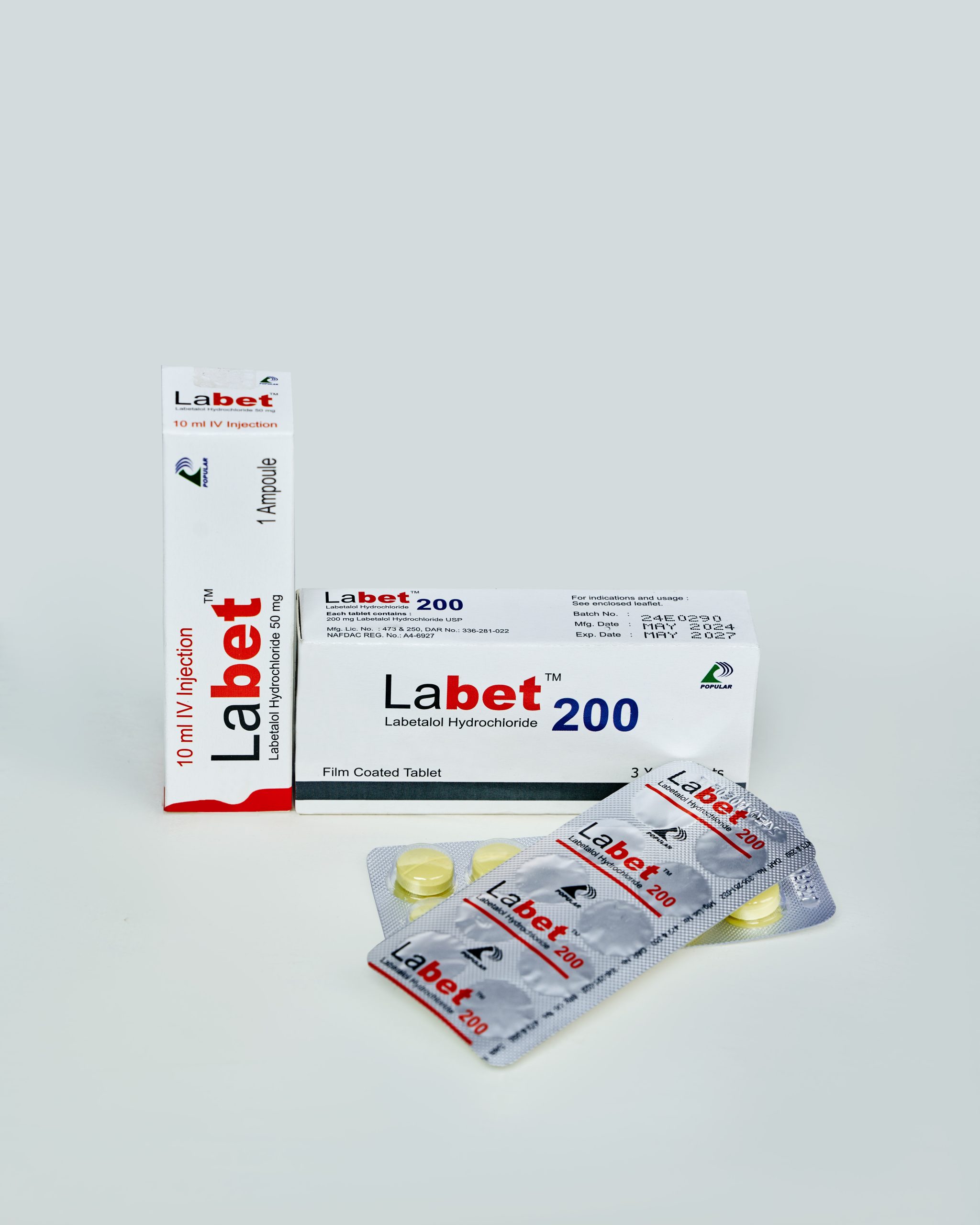
hypertension, and all grades of hypertension (mild, moderate and severe) when oral antihypertensive therapy is desirable. Labetalol tablets are also indicated for the treatment of patients with angina pectoris coexisting with hypertension. Injection: Hypertension (including hypertension ii:i pregnancy, hypertension after stroke, hypertension with angina, and hypertension following acute myocardial infarction); hypertensive crisis; Anesthesia when a hypotensive technique is indicated.
Dosage and Administration
Tablet: initially 100 mg (50 mg in elderly) twice daily with food increased at intervals of 2-3 days to the usual dose of 200 mg twice daily; up to 800 mg daily in 2 divided doses (3 divided doses if higher); maximum 2.4 g daily.
Injection:
Bolus Injection Method: If it is essential to reduce the blood pressure quickly, a test dose of 25 mg should be given by slow intravenous injection (over a period of at least one minute), followed by repeated injections of 50 mg, 75 mg, 75 mg, 75 mg at 10- 20 minutes intervals until the desired BP is reached the maximum cumulative dose that can be given is 300 mg. The maximum effects on BP usually occur within 5 minutes. A maintenance dose of Labet tablets is then commenced at 600 mg daily in 3 divided doses.
Continuous Infusion Method: Labet injection should be diluted with a suitable intravenous infusion fluid to a concentration of 1mg/ml. Compatible fluids include solution of 5°/o dextrose, 0.9% Sodium Chloride and mixture of sodium chloride and dextrose Injection.
The contents of 4 vials (40 ml) are added to 160 ml of compatible fluids. The resultant 200 ml of solution will contain 200 mg labetalol (1mg/ml). The diluted solution should be administered (using an IVAC or a Cardiff infusion pump at a rate of 2 ml/min) to deliver 2 mg/ minute
Side Effects
Adverse effects reported are postural hypotension (avoid upright position during and for 3 hours after intravenous administration), tiredness, weakness, headache, rashes, scalp tingling, difficulty in micturition, epigastric pain, nausea, vomiting; liver damage.
Contraindications
Labetalol is contraindicated for patients known to have hypersensitivity to the medicine. Labetalol Is contraindicated in second- or third-degree heart block, intranodal A-V block, uncontrolled heart failure, sick-sinus syndrome, cardiogenic shock and other conditions associated with severe and prolonged hypotension or severe bradycardia, and bronchial asthma or other obstructive lung disorders.